

In general form the Mealy circuit can be represented with its block schematic as shown in Fig.3.40. a feedback path the state of the sequential circuit (inputs. ECE124 Digital Circuits and Systems, Final Review, Spring 2011. Analysis of synchronous sequential circuits with different types of flip-flops is. The false outputs can be eliminated by allowing input to change only at the active transition of the clock (in our example HIGH-to-LOW). Different types of clocked storage elements are reviewed in this book. Due to this, if the input variations are not synchronized with the clock, the derived output will also not be synchronized with the clock and we get false output (as it is a synchronous sequential circuits). However, they can affect the output of the circuit. 3.39, we can easily realize that, changes in the input within the clock pulses can not affect the state of the flip-flop. 4 analyzed the effects of different graph-based intermediate representations, inclutding binary decision diagram, and-inverter graph. Lec 07 - ANALYSIS OF CLOCKED SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS. 3.39, the output of the circuit is derived from the combination of present state of flip-flops and input (s) of the circuit. sequential logic circuits examples What is state diagram in sequential circuit. When the output of the sequential circuit depends on both the present state of flip-flop(s) and on the input(s), the sequential circuit is referred to as Mealy Circuit.
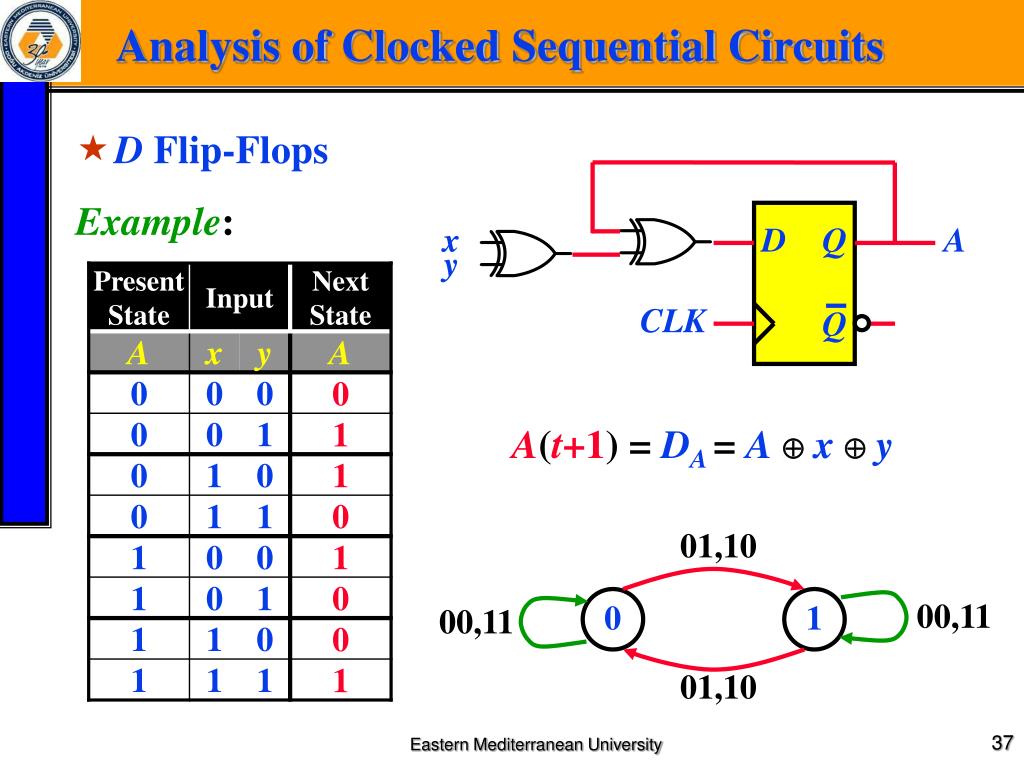
it varies in synchronism with the clock input. In the Moore Circuit, as output depends only on present state of flip-flops, it appears only after the clock pulse is applied, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
